Ransomware is vicious malware that locks users out of their devices or blocks access to files until a sum of money, or ransom, is paid. Ransomware attacks can be deployed in different forms. Some variants may be more harmful than others, but they all have one thing in common: a ransom.
Once the malware is on the machine, it starts to encrypt all data files it can find on the machine itself and on any network shares the PC has access to. Once a user finds that access to the files is blocked and alerts a system admin. The system admin usually finds two files in the directory that indicate the files have been taken hostage, along with instructions on how to pay the ransom to decrypt the files.
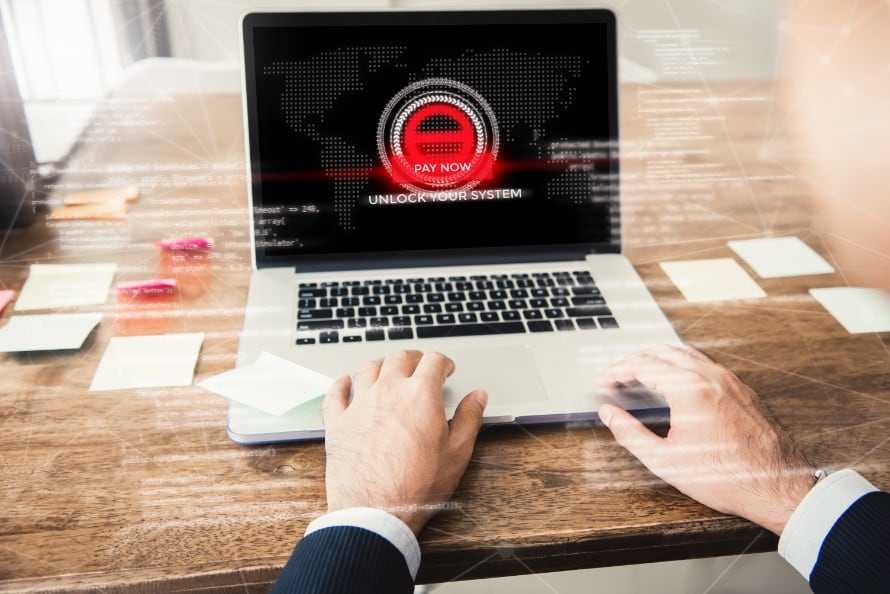

Ransomware can spread across the Internet without specific targets. But the nature of this file-encrypting malware means that cybercriminals also are able to choose their targets. This targeting ability enables cybercriminals to go after those who can — and are more likely to — pay larger ransoms.
Ransomware attacks cause downtime, data loss, and possible intellectual property theft and in certain industries are considered a data breach.
Payments are typically required to be in an untraceable crypto-currency such as bitcoin.
Small to Medium Sized Businesses are attractive targets because they generally do not have the defenses that large enterprises can deploy but are able to afford a $500 to $700 payment to regain access to their files.
While knowing how to fight back if your company is attacked by ransomware is critical, taking proactive steps to minimize the odds that your organization falls victim to ransomware is equally necessary.
There are ways to protect yourself from ransomware.
Preventing ransomware attacks in the first place can save your business tens of thousands of dollars — or perhaps millions — in losses due to interrupted operations, data loss, and other consequences. Here are a list of Do’s and Don’t to help protect against falling victim to a ransomware attack:
- Do use security software. To help protect your data, install and use a trusted security suite that offers more than just antivirus features.
- Do keep your security software up to date. New ransomware variants continue to appear, so having up-to-date internet security software will help protect you against cyberattacks.
- Do update your operating system and other software. Software updates frequently include patches for newly discovered security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by ransomware attackers.
- Don’t automatically open email attachments. Email is one of the main methods for delivering ransomware. Avoid opening emails and attachments from unfamiliar or untrusted sources.
- Do be wary of any email attachment that advises you to enable macros to view its content. Once enabled, macro malware can infect multiple files. Unless you are absolutely sure the email is genuine and from a trusted source, delete the email.
- Do back up important data to an external hard drive. If the victim has backup copies, the cybercriminal loses some advantage. Backup files allow victims to restore their files once the infection has been cleaned up. Ensure that backups are protected or stored offline so that attackers can’t access them.
- Do use cloud services. This can help mitigate a ransomware infection, since many cloud services retain previous versions of files, allowing you to “roll back” to the unencrypted form.
- Do use both firewall and anti-virus software.
- Do not use public Wi-Fi connections unless on a virtual private network or using encryption software.
- Do use the most recent version of your operating system and browser.
- Do train employees on security measures for devices and train to fight against social engineering or phishing attacks.
- Don’t pay the ransom. Keep in mind, you may not get your files back even if you pay a ransom. A cybercriminal could ask you to pay again and again, extorting money from you but never releasing your data.
Other terms related to ransomware:
Scareware – Scareware is fake software that acts like an antivirus or a cleaning tool. Scareware often claims to have found issues on your computer, demanding money to resolve the problems. Some types of scareware lock your computer. Others flood your screen with annoying alerts and pop-up messages.
RaaS – “Ransomware as a service,” is a type of malware hosted anonymously by a hacker. These cybercriminals handle everything from distributing the ransomware and collecting payments to managing decryptors — software that restores data access — in exchange for their cut of the ransom.
Fake law enforcement ransomware locks its victims out of their desktops while showing what appears to be a page from an enforcement agency such as the FBI. This fake page accused victims of committing crimes and told them to pay a fine with a prepaid card.
All about ransomware from Malwarebytes – https://www.malwarebytes.com/ransomware/
What is Ransomware and How Does it Work? – https://www.sentinelone.com/blog/how-does-ransomware-work/
 Tech Tuesday is heard each Tuesday on Mix102.5 with Big Poppa and CCNY Tech Engineer Jake Sears. Since 1988, CCNY Tech has been an IT Hardware Sales and Services company. Ten years ago, CCNY Tech has added IT Asset Disposition to it’s offerings.
Tech Tuesday is heard each Tuesday on Mix102.5 with Big Poppa and CCNY Tech Engineer Jake Sears. Since 1988, CCNY Tech has been an IT Hardware Sales and Services company. Ten years ago, CCNY Tech has added IT Asset Disposition to it’s offerings.






 Tech Tuesday is heard each Tuesday on Mix102.5 with Big Poppa and CCNY Tech Engineer Jake Sears. Since 1988, CCNY Tech has been an
Tech Tuesday is heard each Tuesday on Mix102.5 with Big Poppa and CCNY Tech Engineer Jake Sears. Since 1988, CCNY Tech has been an 
 So many people rely on Internet in their homes while they work remotely or take classes. Strong internet wifi signal can make the difference in a glitchy video conference call or an inability to upload or download an important file.
So many people rely on Internet in their homes while they work remotely or take classes. Strong internet wifi signal can make the difference in a glitchy video conference call or an inability to upload or download an important file.
 Tech Tuesday is heard each Tuesday on Mix102.5 with Big Poppa and CCNY Tech’s Marketing Guru Daryl Ledyard. Since 1988, CCNY Tech has been an
Tech Tuesday is heard each Tuesday on Mix102.5 with Big Poppa and CCNY Tech’s Marketing Guru Daryl Ledyard. Since 1988, CCNY Tech has been an